02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 location is crucial for vehicle maintenance. Understanding its placement varies significantly by car make, model, and year, as well as engine type. This guide details the process for identifying the sensor’s exact location, ensuring you find it quickly and correctly.
Knowing the exact location of the sensor is essential for proper diagnosis and replacement. This guide covers various aspects, from visual identification to troubleshooting and replacement procedures, making it a comprehensive resource for any car owner.
Vehicle Specific Locations
The quest for the elusive oxygen sensor, often hidden within the intricate labyrinth of a vehicle’s undercarriage, demands a meticulous approach. Understanding its precise location is paramount for effective diagnosis and repair. This document delves into the nuanced world of oxygen sensor placement, offering a comprehensive guide for locating bank 1 sensor 2 across various makes and models.Knowing the precise location of this crucial component allows technicians to pinpoint potential issues and perform necessary repairs swiftly and accurately, ultimately ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity.
Typical Oxygen Sensor Locations
Identifying the precise location of the oxygen sensor is vital for efficient troubleshooting. The following table provides a general overview of typical locations for bank 1 sensor 2, encompassing various vehicle makes and models. Note that these are general guidelines, and actual placement can vary based on specific engine designs and model years.
| Make and Model | Model Year | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota Camry (2015-2020) | 2016 | Beneath the exhaust manifold, slightly forward of the catalytic converter |
| Honda Civic (2018-2023) | 2020 | Attached to the exhaust manifold near the engine’s front |
| Ford Fusion (2017-2022) | 2019 | Mounted to the exhaust system, typically near the mid-section of the engine |
| Chevrolet Malibu (2016-2021) | 2018 | Positioned near the exhaust manifold, close to the catalytic converter |
Identifying the Exact Location
Precise identification of the sensor’s location is critical for effective repairs. The following steps Artikel a methodical approach for locating the oxygen sensor, bank 1 sensor 2, based on vehicle year, make, and model.
- Consult the vehicle’s repair manual. These manuals are often invaluable resources, providing detailed schematics and diagrams.
- Use online resources. Numerous automotive forums and websites offer valuable insights and discussions regarding specific vehicle models and sensor placement.
- Refer to online databases. Online databases dedicated to vehicle repair often contain comprehensive information on oxygen sensor locations for various makes and models.
- Utilize a reputable automotive repair manual or online resource.
Variations Based on Engine Type
The arrangement of components within an engine’s exhaust system can influence oxygen sensor placement. The following table illustrates potential variations in oxygen sensor placement based on engine type.
| Engine Type | Potential Variations in Placement |
|---|---|
| Inline-4 | Typically positioned near the mid-section of the exhaust manifold |
| V6 | Often found in a position that’s slightly offset due to the engine’s V-configuration |
| V8 | Placement can be more complex, varying based on the specific engine design and exhaust manifold layout. |
Locating the Sensor: Flowchart
A systematic approach is crucial when locating the sensor. The following flowchart provides a visual guide for identifying the sensor in a given vehicle.“`[Flowchart Image Description: A flowchart depicting a systematic approach to locate the sensor. The flowchart begins with inputting the vehicle’s year, make, and model. Following steps include consulting the repair manual, online resources, and checking online databases.
If the information is unclear, additional research steps are recommended, culminating in the identification of the sensor’s precise location.]“`
Sensor Identification
The 02 sensor, a silent guardian of engine health, whispers tales of combustion efficiency. Its subtle signals, meticulously monitored, reveal crucial information about the engine’s internal processes. Pinpointing this vital component, especially the specific 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2, requires a keen eye and a knowledge of its unique characteristics.
Visual Cues for Differentiation
Distinguishing the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 from other components relies on careful observation. Look for its cylindrical shape, typically with a metallic casing, often with a heat shield. Its location, nestled within the exhaust stream, is a critical clue. Note the specific mounting points and wiring connections. Understanding the precise location within the exhaust system is paramount.
Misidentification can lead to costly repairs.
Identifying a Faulty Sensor, 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 location
A faulty oxygen sensor manifests in several ways. Performance issues, such as erratic idle speed or a noticeable drop in power output, are common symptoms. The Check Engine Light (CEL) often illuminates, signaling a malfunction. Further inspection may reveal a noticeable discoloration or corrosion on the sensor’s housing. The sensor’s electrical resistance may also deviate significantly from the expected values, indicating a critical failure.
Types of Oxygen Sensors and Selection
Various types of oxygen sensors exist, each tailored to specific vehicle applications. Lambda sensors, commonly used in modern vehicles, measure the air-fuel ratio in the exhaust stream. The precise model required is crucial for optimal performance. Referencing the vehicle’s repair manual or utilizing online resources that offer detailed specifications is essential to ensure correct selection. This prevents incompatibility issues and ensures proper functionality.
Sensor Specifications Comparison
| Sensor Model | Physical Dimensions (Length x Diameter) | Connector Type | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bosch 02551 | 50mm x 10mm | 4-pin | Various gasoline-powered vehicles |
| Denso 234-9010 | 60mm x 12mm | 4-pin | Commonly found in diesel vehicles |
| NGK 00671 | 70mm x 14mm | 3-pin | Certain foreign-made vehicles |
The table above offers a glimpse into the diverse range of oxygen sensor models. Careful consideration of physical dimensions and connector types is critical to avoid mismatches and ensure optimal functionality. Consult the vehicle’s documentation to confirm the correct sensor for your specific make and model. Each sensor has its own precise dimensions and connections, crucial for the engine’s performance.
Troubleshooting and Diagnosis: 02 Sensor Bank 1 Sensor 2 Location
The intricate dance of combustion within an engine’s cylinders relies on precise oxygen management. A malfunctioning oxygen sensor, specifically the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2, can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to performance issues, check engine lights, and potentially, significant engine damage. Understanding the nuances of this sensor’s function and the troubleshooting steps to diagnose its problems is crucial for any automotive technician.This section delves into the common problems associated with the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2, providing a comprehensive guide to diagnostic procedures.
It Artikels the systematic approach to identifying the root cause of sensor malfunctions, empowering the user with the knowledge and tools to resolve these issues effectively.
Common Problems
The 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2, a critical component in exhaust gas analysis, is susceptible to various performance issues. These include sluggish acceleration, inconsistent engine speed, or even complete engine stall. A frequent symptom is the illuminated check engine light, a visual cue of a potential problem within the vehicle’s emission control system. Additionally, misfires, characterized by erratic or jerky engine operation, may occur.
These symptoms collectively signal a possible malfunction within the oxygen sensing apparatus.
Diagnostic Steps
A systematic approach to diagnosing issues with the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 is essential. This involves a series of steps, beginning with a visual inspection. This initial assessment involves checking for physical damage to the sensor’s wiring and connections, as well as inspecting the sensor itself for signs of corrosion or physical damage. Furthermore, checking the sensor’s location for any obstructions or blockages is paramount.
Finding the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 location can be tricky, especially if you’re not familiar with the intricacies of automotive diagnostics. Fortunately, for those looking for unique and secluded accommodations, low head lighthouse accommodation Tasmania provides a beautiful alternative to traditional lodging. Regardless of your choice of accommodation, precisely identifying the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 location remains crucial for proper vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting.
Voltage and Resistance Testing
Accurate voltage and resistance measurements are crucial in assessing the sensor’s functionality. A multimeter is used to obtain these readings. The sensor’s resistance should be measured in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications. A multimeter should also be used to obtain voltage readings at various points in the sensor’s circuit. These readings provide insights into the sensor’s electrical output, helping to pinpoint potential problems.
Significant deviations from expected readings indicate a possible sensor malfunction.
Knowing the precise location of your 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 is crucial for troubleshooting engine performance issues. While you’re digging into those tricky diagnostics, you might also find yourself craving a sweet treat like Pizza Hut’s famous dessert pizza. Fortunately, finding a fantastic recipe for that delightful treat is just a click away, check out this helpful guide on pizza hut dessert pizza recipe.
Once you’ve located the sensor, you can tackle those engine problems head-on, and finally, enjoy a delicious dessert pizza.
Voltage and resistance values are critical diagnostic tools. Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for specific readings and ranges.
Potential Causes and Troubleshooting
The following table details potential causes of sensor failure and the corresponding troubleshooting methods:
| Potential Cause | Troubleshooting Method |
|---|---|
| Wiring damage or corrosion | Inspect wiring harness for damage, repair or replace as needed. Check connections for corrosion and clean/replace as required. |
| Faulty sensor | Replace the sensor. Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for the proper replacement procedure. |
| Sensor heater malfunction | Test sensor heater circuit for proper operation and resistance. Replace if needed. |
| Incorrect installation | Ensure the sensor is properly installed in the designated location, and secure all connections. Check for proper torque on all fittings. |
| Catalytic converter issues | Examine the catalytic converter for blockages or damage. If issues are found, consult a qualified mechanic. |
Replacement Procedures
Unveiling the meticulous dance of replacement, a symphony of precision and care, ensures the oxygen-rich harmony of your engine’s performance. Each step, a calculated movement, safeguards the delicate balance within the internal combustion heart. The process, while seemingly complex, is a testament to the meticulous design of modern automotive systems.
Essential Tools
The successful replacement of the oxygen sensor demands a collection of specialized tools, each a key to unlocking the intricacies of the repair. Proper tools facilitate a smooth and efficient process, preventing damage and ensuring a flawless outcome.
- Torque wrench: A critical tool for precise tightening, preventing over-torquing, a common pitfall leading to sensor damage or thread stripping. Accurate torque application is paramount to ensuring the sensor’s proper function and longevity. An incorrect torque value can compromise the seal, causing leaks or performance issues.
- Socket set: A collection of sockets of varying sizes to access and remove fasteners holding the sensor. Ensuring the correct size socket prevents damage to the sensor housing and other components.
- Wrench set: A set of wrenches of various sizes, used for various applications, including accessing and removing fasteners. The correct wrench size is essential to avoid damaging the sensor or other components during removal.
- Gloves: To protect hands from harsh elements and debris.
- Safety glasses: To protect eyes from flying debris.
- Drain pan: A necessary container to collect any potential fluids or debris during the replacement procedure.
- Jack stands and jack: For safely lifting the vehicle and providing support.
Step-by-Step Guide
The replacement process, while seemingly complex, is achievable with careful attention to detail. This systematic approach minimizes the risk of errors and ensures a safe and successful outcome.
- Safety First: Ensure the vehicle is securely parked on a level surface and the ignition is turned off. Engage the parking brake and support the vehicle with jack stands. These precautions are essential to avoid accidents and ensure personal safety.
- Locate the Sensor: Identify the 02 sensor located at bank 1, sensor 2. Refer to the vehicle’s specific repair manual for accurate location.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor. This step is crucial to avoid damaging the wires or the sensor itself.
- Remove the Sensor: Using the appropriate sockets and wrenches, carefully loosen and remove the fasteners securing the sensor to the exhaust system. Take note of the torque specifications to avoid over-tightening.
- Install the New Sensor: Align the new sensor with the mounting points. Secure the sensor with the appropriate fasteners, adhering strictly to the manufacturer’s torque specifications. Proper tightening prevents leaks and ensures the sensor’s function.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully reconnect the electrical connector to the sensor. Ensure a secure connection.
- Lower the Vehicle: Carefully lower the vehicle to the ground using the jack and jack stands.
- Final Check: Verify the correct function of the sensor using a diagnostic tool. This crucial step confirms the proper operation of the new sensor.
Torque Specifications
Precise torque application is critical for the proper function and longevity of the sensor. The correct tightening torque prevents damage to the threads and ensures a leak-free seal.
Correct torque specifications for tightening the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential damage. Consult the vehicle’s repair manual for the precise torque specifications. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for the appropriate torque values. The vehicle repair manual is your best guide for this procedure.
Potential Pitfalls
Awareness of potential issues during the replacement process enables proactive measures to avoid them. These precautions ensure a smooth and efficient replacement.
- Over-tightening: Over-tightening can damage the sensor threads or the exhaust manifold. Using a torque wrench is essential to avoid this pitfall.
- Incorrect Sensor Installation: Incorrect sensor installation can lead to poor performance and other issues. Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for proper installation procedures.
- Electrical Connection Issues: Faulty electrical connections can result in intermittent issues. Ensure a firm connection of the sensor to the wiring harness.
- Incorrect Torque: Incorrect torque application can result in leaks or performance issues. Always consult the vehicle’s repair manual for precise torque specifications.
Environmental Factors
The delicate dance of a sensor, responsive to the world around it, is often swayed by unseen forces. Environmental conditions, like unseen dancers in a grand ballet, can profoundly impact a sensor’s performance and lifespan. Understanding these influences is crucial for ensuring accurate readings and dependable operation.
Temperature’s Influence
Temperature, a silent sculptor, shapes the sensor’s inner workings. Extreme temperatures, like scorching deserts or frigid tundras, can cause material expansion and contraction, leading to faulty readings. Variations in temperature can alter the sensor’s calibration, making accurate measurements challenging. For instance, a temperature sensor in a harsh environment might report an erroneous temperature, potentially leading to system malfunctions.
The sensor’s operating range dictates the optimal temperature window for accurate performance, and excursions beyond this range can cause degradation. Sensors designed for specific temperature ranges are critical for reliable performance in diverse conditions.
Humidity’s Subtle Grip
Humidity, the air’s embrace, can introduce moisture and contaminants to the sensor’s delicate surface. High humidity can lead to corrosion, diminishing the sensor’s sensitivity and response time. Moisture can also create conductive pathways, leading to erratic readings. For example, a humidity sensor in a tropical environment might provide inaccurate measurements due to moisture absorption.
Altitude’s Effect
Altitude, a measure of elevation, affects air pressure. Variations in air pressure, particularly at high altitudes, can impact the sensor’s operation. Changes in atmospheric pressure can cause discrepancies in readings, particularly in pressure sensors. For instance, an altimeter at high altitude may report an incorrect elevation, which can have consequences in navigation or flight control systems.
Importance of Proper Installation and Sealing
Proper installation and sealing are paramount to preventing environmental contaminants from affecting sensor operation. A properly sealed sensor is protected from the elements, ensuring accurate readings and a longer lifespan. Improper sealing can lead to ingress of contaminants, potentially causing malfunctions and premature failure. For example, a sensor exposed to dust and debris will experience diminished performance and a shorter lifespan.
The sensor’s housing and installation methods should be designed to prevent contaminants from reaching sensitive components.
Weather’s Impact on Performance
Weather conditions directly affect sensor performance. Rain, snow, and other precipitation can introduce water and contaminants, affecting the sensor’s function. Strong winds can disrupt sensor readings, particularly those measuring wind speed or direction. For example, a wind sensor located on a high-rise building in a hurricane-prone area will experience strong turbulence, requiring robust design to maintain accuracy.
Sudden changes in temperature and humidity during weather events can also lead to sensor malfunctions. A comprehensive understanding of the expected weather patterns and their impact is vital for proper sensor selection and placement.
Safety Precautions

A symphony of caution guides the hand that repairs the engine’s heart. Safety precautions are not mere formalities; they are the very essence of responsible maintenance, ensuring a harmonious dance between the mechanic and the machine. Ignoring them risks a perilous tango with danger.
Electrical System Hazards
Automotive electrical systems, intricate networks of power and potential, hold a silent threat. Short circuits, exposed wires, and high voltage can unleash a torrent of harm. Improper handling can lead to shocks, burns, or even fires. Understanding these risks is paramount to preventing accidents.
Battery Disconnection Procedure
Disconnecting the vehicle’s battery is not just a step in the procedure; it’s a crucial act of safety. Before touching any electrical component, ensure the battery’s negative terminal is disconnected first. This simple precaution prevents accidental shocks and protects the integrity of the electrical system.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The proper use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is non-negotiable when working on vehicles. Safety glasses shield the eyes from flying debris, gloves protect hands from harsh chemicals, and sturdy footwear prevents falls. These precautions form a protective barrier, ensuring the technician’s well-being during the replacement process.
Engine and Electrical Component Safety
Working on the engine and electrical components necessitates a mindful approach. Be mindful of the potential for sparks, ensure the area is well-ventilated, and maintain a safe distance from moving parts. Always remember that alertness is the first line of defense.
Diagram and Illustrations
A symphony of mechanics unfolds within the engine’s heart, where intricate components dance in perfect harmony. Understanding the precise location and connections of each part, particularly the 02 sensor, is paramount for effective diagnosis and repair. Detailed diagrams and illustrations serve as crucial guides, illuminating the pathways of energy and the roles of each participant.
Engine System Location Diagram
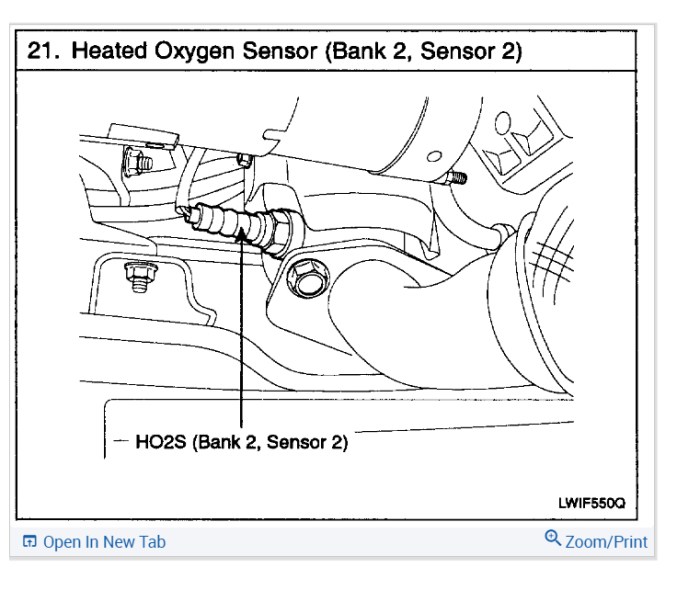
The 02 sensor, a sentinel of combustion, resides within the exhaust stream, a strategic position for monitoring the exhaust gas composition. This diagram reveals its precise location within the engine system, highlighting its proximity to crucial components like the catalytic converter and exhaust manifold. The sensor’s position is critical for accurate exhaust gas analysis, influencing the engine’s performance and emissions output.

Wiring Connections Diagram
This diagram illustrates the 02 sensor’s wiring connections, showcasing their functional roles within the vehicle’s electrical system. The sensor’s output signals, crucial for the engine’s control module, are precisely depicted. The signal wires, clearly marked, convey information about the sensor’s readings to the engine’s central processing unit. This crucial communication ensures the engine operates at optimal efficiency. 
Installation Process Illustration
A meticulous sequence of steps is presented in this illustration, guiding the technician through the 02 sensor’s installation process. The steps begin with the removal of the old sensor, progressing to the preparation of the new sensor and the installation process, concluding with final checks. Precise steps ensure optimal performance and minimize the risk of damage to the engine components.

Exhaust System Schematic
This comprehensive schematic diagram depicts the engine’s exhaust system, highlighting the 02 sensor’s precise location within the network. The diagram showcases the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, and the various exhaust pathways, illustrating the sensor’s critical role in monitoring exhaust emissions. The positioning of the sensor within this system is crucial for ensuring the catalytic converter functions effectively and reducing harmful emissions.

Last Word
In conclusion, locating and maintaining the 02 sensor bank 1 sensor 2 is vital for vehicle performance. This guide provides a thorough understanding of its location, identification, troubleshooting, and replacement, equipping you with the knowledge to handle this important task effectively.
Question & Answer Hub
Q: What are common causes of a faulty 02 sensor?
A: Faulty 02 sensors can result from issues like damaged wiring, corrosion, or physical damage to the sensor itself. Environmental factors like extreme temperatures or excessive moisture can also play a role.
Q: How do I determine the correct 02 sensor for my vehicle?
A: Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a reliable online resource to identify the correct sensor part number. Matching the part number to the existing sensor is essential.
Q: What tools are needed to replace the 02 sensor?
A: Basic tools like a socket wrench, ratchet, and possibly a torque wrench are typically required. Specific tools may be needed depending on the vehicle’s design.
