P0340 Nissan Bank 1 location is a crucial diagnostic concern for many Nissan vehicle owners. This guide delves into the complexities of this fault code, exploring the precise location of Bank 1 within the engine, the function of the crankshaft position sensor, and the diagnostic steps to identify and resolve the issue. Understanding the intricacies of this code is key to effectively repairing the vehicle and restoring its optimal performance.
The information presented will offer a clear pathway for diagnosing and resolving this issue.
This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the path to resolving P0340 Nissan Bank 1 location issues. We will explore the intricacies of the crankshaft position sensor, its role within the engine’s function, and its specific location within Bank 1. This knowledge will equip you with the necessary tools to diagnose and rectify this common issue.
Understanding the P0340 Code: P0340 Nissan Bank 1 Location
Yo, fam! So, you’re gettin’ that dreaded P0340 code on your Nissan? Don’t freak out, it’s a common issue, and we’re gonna break it down for you, straight from the source. This code usually means there’s a problem with the crankshaft position sensor, which is a crucial part of your engine’s brain. Let’s dive in!
Crankshaft Position Sensor Function
The crankshaft position sensor is like the engine’s GPS. It tells the engine control module (ECM) exactly where the crankshaft is in its rotation. This information is vital for timing the fuel injection and ignition, ensuring the engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Think of it as the sensor’s job to precisely pinpoint the crankshaft’s position, allowing the engine to operate in harmony.
Without accurate information, the engine’s computer struggles to coordinate everything properly.
P0340 Code Meaning
The P0340 code signifies a problem with the crankshaft position sensor. It indicates that the ECM is detecting an erratic or incorrect signal from the sensor, causing it to throw the error code. Basically, the sensor isn’t reporting the crankshaft’s position accurately, leading to a miscommunication between the sensor and the engine’s computer.
Common Symptoms
A P0340 code often manifests with noticeable symptoms. You might experience rough idling, engine misfires, hesitation during acceleration, or even complete engine stalling. Sometimes, the check engine light will blink or illuminate constantly. It’s like the engine’s trying to communicate something’s wrong. It might even feel like the car’s struggling to respond to the gas pedal.
Potential Causes
- Sensor Issues: The sensor itself could be faulty, worn out, or damaged. It’s like a faulty GPS that’s constantly giving incorrect directions. Over time, the sensor can lose its accuracy, leading to a P0340 code. It could also be due to environmental factors or physical damage to the sensor.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can interfere with the signal from the sensor to the ECM. It’s like a broken phone line – the message can’t get through. This is another common culprit, and you’d need to check the wiring harness and connections thoroughly.
- ECM Issues: Although less common, the ECM itself can sometimes be the culprit. It could be a software glitch or a hardware malfunction in the engine control unit, causing it to misinterpret the signal from the sensor. It’s a bit like a faulty computer program that doesn’t understand the instructions from the sensor.
- Other Related Components: Other components related to the crankshaft position sensor’s function, such as the engine mount or the timing chain, can also contribute to a P0340 code. It’s like a domino effect; a problem in one area can impact other components, causing the crankshaft position sensor to malfunction.
Diagnostic Steps
- Check the Sensor’s Connection: Inspect the wiring connections and make sure they’re clean and secure. Loose connections can be a quick and easy fix, so this is the first step to look at.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the sensor for any visible damage, corrosion, or signs of physical wear. It’s important to visually check the sensor to see if it’s physically damaged or showing signs of wear and tear.
- Scan the Code: Use a diagnostic scanner to retrieve the specific P0340 code and any additional codes. It’s important to scan the code for other errors or problems that might be present.
- Test the Sensor: A professional mechanic can use specialized diagnostic tools to test the sensor’s output and determine if it’s functioning correctly. It’s important to use specialized diagnostic tools to test the sensor and ensure that it’s working correctly.
- Replace the Sensor (If Necessary): If the sensor is faulty, it needs to be replaced with a genuine part to ensure proper engine function. It’s important to use genuine parts to ensure that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Bank 1 Location in Internal Engine Components
Yo, fam! So, you’ve got the P0340 code sorted, now let’s dive into where Bank 1 sits in your Nissan engine. Knowing this crucial location is key to pinpointing the problem if you’re having engine issues. This breakdown will give you the lowdown on Bank 1’s components and how it plays a role in the overall engine function.Bank 1 is essentially one side of your Nissan engine’s cylinders.
Think of it like a team, Bank 1 and Bank 2 working together to power the car. Understanding their individual roles and components is crucial for troubleshooting. This isn’t just some random number; it’s a specific reference point used by mechanics to pinpoint problems.
Bank 1 Cylinder Arrangement
Bank 1 is the group of cylinders on one side of the engine block. This arrangement affects how the engine components are positioned. This specific layout is critical for proper combustion and fuel delivery, which directly impacts the engine’s performance. For instance, in some V6 engines, Bank 1 is the left side of the engine, while in an inline-4 engine, the numbering is just an arrangement for the firing order.
Components Typically Associated with Bank 1
Understanding the components specific to Bank 1 is essential for diagnosing problems. This includes the spark plugs, injectors, and associated wiring that feed into the engine cylinders. These components directly interact with the fuel and air mixture, and any issues with them will impact the overall performance.
Diagnosing a P0340 Nissan bank 1 location code often involves scrutinizing the crankshaft position sensor’s placement, a crucial component for accurate engine timing. This intricate process, similar to calibrating the delicate balance of flavors in a recipe for basil ice cream recipe for basil ice cream , requires understanding the sensor’s precise location within the engine’s complex network.
Correctly identifying the P0340 code’s origin, like mastering the perfect balance of basil and cream, ultimately leads to efficient engine performance.
- Spark Plugs: These ignite the fuel-air mixture in each cylinder. Faulty spark plugs on Bank 1 can lead to misfires and reduced power output on that side of the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: These precisely deliver fuel into each cylinder. Issues with injectors on Bank 1 could cause uneven combustion and fuel efficiency problems on that bank.
- Crank Shaft Position Sensor (CKP): This sensor is crucial for the engine’s timing. Its location in relation to Bank 1 is vital for accurate timing signals. The CKP sensor measures the rotation speed and position of the crankshaft, a vital signal for the engine control unit (ECU).
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) Location Relative to Bank 1
Imagine a line drawn down the center of the engine block. The crankshaft position sensor (CKP) is usually positioned near the crankshaft itself, often close to the front of the engine block, either near or on the bank 1 side. This positioning is key to its role in detecting the crankshaft’s position. The sensor’s proximity to the crankshaft ensures it receives precise and timely signals, enabling the ECU to control the engine’s function accurately.
| Component | Location |
|---|---|
| Crankshaft | Central to the engine, rotating |
| Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) | Near the crankshaft, often near or on Bank 1 |
Bank 1 and Engine Function
Bank 1 plays a crucial role in the overall engine function. Its cylinders, when working properly in conjunction with Bank 2 (if applicable), contribute to the smooth, powerful operation of the engine. The coordinated firing of pistons in Bank 1 (and Bank 2) creates the torque and power that moves the vehicle. A problem with Bank 1 will manifest as a loss of power, or misfires, on that side of the engine.
Differences Between Bank 1 and Bank 2
In some Nissan engines, Bank 1 and Bank 2 might have slight variations in components. For instance, the intake and exhaust manifolds might be slightly different in their design, or there could be differences in the fuel injector placement or the ignition coil wiring. These differences are usually minimal and depend on the engine’s specific design. These differences are usually minimal, and depend on the specific engine design.
Diagnostic Procedures and Troubleshooting

Yo, so you got that P0340 code on your Nissan? Bank 1 crankshaft position sensor is screwin’ things up, right? Let’s get into the nitty-gritty of diagnosing and fixing this issue. This ain’t rocket science, but precise steps are key to getting it sorted.This section details the systematic approach to identify and rectify problems with the crankshaft position sensor in Bank 1.
Understanding the specific procedures for testing, inspecting, and troubleshooting the sensor will ensure you fix the problem quickly and effectively.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Testing Procedures
To nail down the issue with the crankshaft position sensor, a systematic approach is crucial. This involves checking the sensor’s wiring, connections, and the sensor itself. This ensures a precise diagnosis, avoiding unnecessary replacements.
- Visual Inspection of Wiring and Connectors: Start by visually inspecting all wiring harnesses and connectors associated with the crankshaft position sensor. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, broken connectors, or corrosion. These issues can cause intermittent or complete signal loss, leading to the P0340 code. Pay close attention to areas where the wiring runs through tight spots or near potential sources of heat or vibration.
- Voltage and Resistance Readings: Use a multimeter to check the voltage and resistance readings at the sensor connector. Specific voltage and resistance values are crucial to determining if the sensor is working correctly. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual for the correct specifications. These readings should fall within the manufacturer’s specifications. If not, it could indicate a faulty sensor or a wiring issue.
Deviations from the normal range can point to the source of the problem.
- Isolating Electrical Issues: If voltage or resistance readings are outside the expected range, isolate electrical issues. Check for any short circuits or grounds in the wiring harness. You can use a multimeter to check for continuity between wires. If a short circuit is detected, address the issue immediately. This step is crucial to prevent further damage to the electrical system.
- Sensor Replacement Strategies: If all other checks come back negative, the crankshaft position sensor itself might be faulty. Consider replacing the sensor. Some sensors are easier to access than others. Always consult your vehicle’s repair manual for specific replacement procedures. If replacing the sensor, ensure you use the correct part number and installation method for optimal performance.
Different repair methods have their own advantages and disadvantages; consider the repair’s cost-effectiveness and time constraints.
Sensor Replacement Considerations
Replacing the crankshaft position sensor often involves careful handling and specific installation procedures.
- Tools and Materials: Ensure you have the necessary tools, such as a socket wrench set, a multimeter, and the correct replacement sensor. Having the right tools and materials ensures a smooth and efficient replacement process.
- Installation Procedure: Follow the detailed installation procedure in your vehicle’s repair manual to avoid any complications. This ensures proper sensor function and prevents further issues. Thoroughly tighten all connections after installation.
- Verification after Replacement: After replacing the sensor, verify its functionality by checking the voltage and resistance readings at the connector. This step ensures the replacement was successful. Confirm the P0340 code is gone and the engine runs smoothly.
Potential Solutions and Repairs
Yo, so you got that pesky P0340 code, huh? It’s basically telling you the crankshaft position sensor in Bank 1 is acting up. No worries, we’ll break down the potential fixes and get you back on the road. Think of it like a detective work, but with car parts instead of crimes. We’ll figure out what’s wrong and get it sorted out.This section dives into troubleshooting and repairing sensor issues, wiring problems, and ECM resets, along with alternative solutions for the P0340 code.
We’ll cover everything from replacing the sensor itself to fixing any damaged wiring, all while keeping it simple and easy to understand. Let’s get this done!
Diagnosing a P0340 code in a Nissan, pinpointing the bank 1 location within the engine’s complex circuitry, often reveals underlying mechanical issues. Simultaneously, understanding market fluctuations can impact real estate values, as seen in the current listings for bank foreclosures for sale in Lake Keowee, bank foreclosures for sale in lake keowee , potentially affecting the overall financial picture of the region.
This nuanced understanding is critical when examining the intricate workings of the crankshaft position sensor, ultimately leading to a more thorough diagnosis of the P0340 Nissan bank 1 location problem.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement in Bank 1
Replacing the crankshaft position sensor is a common fix for the P0340 code. This sensor is crucial for the engine control module (ECM) to understand the engine’s speed and position. A faulty sensor can cause a whole host of issues, from rough idling to complete engine misfire.To replace the sensor, you’ll need the right tools, like a socket set, a wrench, and potentially a torque wrench for precise tightening.
Always consult your car’s repair manual for the exact specifications. Properly replacing this part is key to avoiding further problems. It’s essential to have the right tools and know-how to do it correctly. Incorrect replacement can lead to further issues.
- First, locate the sensor’s position on your car’s engine. It’s usually on or near the crankshaft. Refer to your car’s manual for the exact location.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove any bolts or fasteners securing the sensor to the engine. Use the right size socket wrench to avoid damaging the engine or sensor.
- Carefully remove the old sensor. Be gentle; avoid damaging surrounding components.
- Install the new sensor. Ensure the sensor is properly seated and aligned. The new sensor usually comes with a gasket, use it.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Tighten the bolts or fasteners to the specified torque values in your car’s manual.
- Reconnect all related electrical connections. Double-check all connections.
Repairing Damaged Wiring Harnesses or Connectors in Bank 1
Damaged wiring or connectors in the Bank 1 circuit can also cause the P0340 code. Identifying and fixing these issues is crucial for restoring proper engine function. A visual inspection is often the first step.
- Inspect the wiring harness and connectors in Bank 1 for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, broken connectors, or corrosion. Pay close attention to the areas around the sensor, and check for any exposed wires.
- If you find damaged wires, carefully repair or replace them using the appropriate automotive wiring techniques. Using the right gauge of wire and connectors is important. Use heat shrink tubing to seal the connections and prevent future issues.
- Check the connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion. Clean the contacts with a wire brush and dielectric grease if necessary. This helps ensure proper electrical conductivity.
- Ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated to prevent short circuits or electrical problems.
Resetting the Engine Control Module (ECM)
After making repairs, resetting the ECM is essential to ensure the system recognizes the changes. This step ensures the ECM recalibrates and the new sensor or wiring configurations are properly registered.
- Consult your car’s repair manual for the specific ECM reset procedure. Different cars have different methods.
- Usually, it involves a specific sequence of actions, like holding certain buttons or using a scan tool. Follow the steps in your manual closely to avoid any mistakes.
- After the reset, test the engine to verify that the P0340 code has been cleared.
Alternative Solutions
Sometimes, the P0340 code might not be directly related to the sensor or wiring. Other possible causes include problems with the engine’s mechanical components or the ECM itself. Diagnosing the exact problem is important.
- A thorough inspection of all related components in the Bank 1 circuit can help determine the root cause.
- Consult your car’s repair manual for possible alternative solutions or additional diagnostic steps.
Visual Representation of the Components
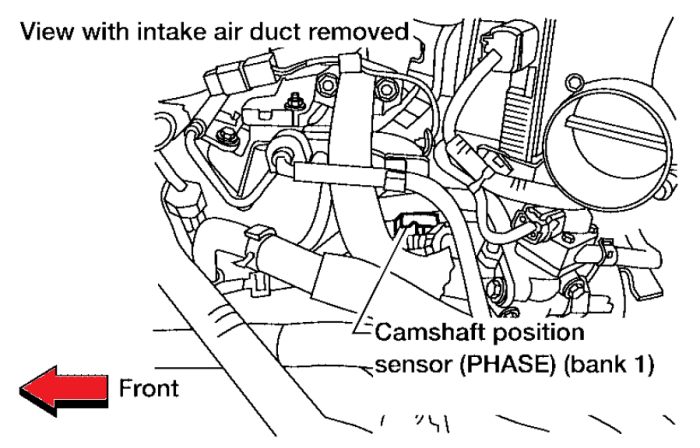
Yo, so we’ve cracked the P0340 code, now let’s visualize the parts involved in that crankshaft position sensor circuit for Bank 1. Knowing the components and their positions is crucial for accurate troubleshooting. This visual breakdown will help you pinpoint the problem faster than you can say “Wah, gawat!”.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Components (Bank 1)
This table lays out the key parts in the Bank 1 crankshaft position sensor circuit. Knowing these components and their part numbers is essential for ordering replacements or just understanding the system.
| Part Name | Part Number | Description | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crankshaft Position Sensor | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | Measures the crankshaft’s rotational position. | Mounted on the engine block near the crankshaft. |
| Wiring Harness | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | Connects the sensor to the engine control module (ECM). | Runs throughout the engine bay. |
| Connector | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | Provides electrical connection to the sensor. | Located on the sensor and wiring harness. |
| Engine Control Module (ECM) | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | Processes signals from the sensor. | Located within the engine bay. Usually in a sealed box. |
Crankshaft Position Sensor Voltage and Resistance Readings (Bank 1)
These readings help determine if the sensor is functioning correctly. It’s crucial to get these right for a proper diagnosis.
| Test Condition | Expected Value | Actual Value | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Output Voltage (engine running) | 0.5V to 5V | (Your reading) | If outside expected range, check wiring and sensor connections. |
| Sensor Resistance (engine off) | (Specific value for your sensor) | (Your reading) | If different, replace the sensor. |
| Sensor Output Signal (engine running) | Signal pattern as per manufacturer specifications | (Your reading – Observe the waveform using an oscilloscope if available) | If not as expected, check wiring and sensor connections. A faulty sensor will often show irregular waveforms. |
Possible Causes, Symptoms, and Troubleshooting Steps for P0340, P0340 nissan bank 1 location
This table Artikels potential causes, noticeable symptoms, and steps to diagnose and fix the issue. You need to figure out the specific cause.
| Cause | Symptom | Troubleshooting Step | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faulty Crankshaft Position Sensor | Check engine light illuminates, rough idle, or engine misfire | Verify voltage and resistance readings using a multimeter. | Replace the crankshaft position sensor. |
| Damaged Wiring | Intermittent check engine light, weak or no signal | Inspect the wiring harness for damage or loose connections. | Repair or replace damaged wiring. |
| ECM Issues | Check engine light is on continuously, erratic engine behavior | Verify the ECM is receiving a signal from the sensor. | Check ECM or possibly replace. |
Comparing Bank 1 and Bank 2 Crankshaft Position Sensors
This table highlights the key differences between the sensors for each bank. Knowing these differences can help you pinpoint issues.
| Component | Bank 1 | Bank 2 | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crankshaft Position Sensor | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | Identical sensors are rare. Sometimes, a Bank 2 sensor might have a slightly different mounting angle or wire connections. |
| Wiring Harness | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | (Specific part number for your Nissan model) | Usually, wiring harnesses are identical. But differences exist in some models. |
| ECM Connections | Specific connections to the ECM. | Specific connections to the ECM. | ECM connections differ based on the sensor’s signal. |
Detailed Descriptions of Bank 1 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Parts
The crankshaft position sensor is a crucial component in your Nissan’s engine management system. It precisely measures the crankshaft’s rotational speed and position. This information is vital for the engine control module (ECM) to regulate ignition timing, fuel injection, and other engine functions. A faulty sensor can lead to a host of problems.
The wiring harness is a complex network of wires that connects the crankshaft position sensor to the engine control module. Any damage or corrosion to the wiring can disrupt the electrical signal, resulting in inaccurate readings. The harness needs to be intact to relay the information correctly.
The connector provides the crucial electrical connection between the sensor and the wiring harness. A damaged or corroded connector can cause intermittent signal problems, and the sensor won’t work properly. Inspect the connector carefully.
The engine control module (ECM) is the brain of your engine. It receives signals from various sensors, including the crankshaft position sensor. The ECM then uses this information to adjust the engine’s operation in real-time. A malfunctioning ECM can affect the performance of the entire engine.
Final Summary
In conclusion, understanding the P0340 Nissan Bank 1 location code involves a multifaceted approach. This guide has explored the sensor’s function, its position in Bank 1, and the diagnostic steps necessary to pinpoint the source of the problem. By following the provided procedures, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve this issue, restoring optimal engine performance. Remember that accurate diagnosis and repair are crucial for maintaining the longevity and reliability of your Nissan vehicle.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a P0340 code?
Common symptoms include rough idling, misfires, hesitation during acceleration, and engine stalling. These symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the underlying issue.
What is the role of the crankshaft position sensor?
The crankshaft position sensor provides crucial information to the engine control module (ECM) about the crankshaft’s position and speed. This information is essential for precise engine timing and fuel delivery.
How do I locate Bank 1 in my Nissan engine?
Bank 1 is typically the cylinder bank on the driver’s side of the engine. Refer to your specific Nissan vehicle’s repair manual for a precise identification.
What are the potential causes of a P0340 code?
Potential causes range from faulty crankshaft position sensors to wiring issues, and even problems with the engine control module itself. This guide provides diagnostic steps to isolate the specific cause.
